SE Lifecycle
- Research:
- Open-source intelligence (OSINT) gathering.
- Identifying vulnerabilities (e.g., social media oversharing).
- Dumpster Diving (Collecting
discardedsensitivematerials) - Technical Research (
vendors)
SE Lifecycle
- Research:
- Examples
- Identifying a
target’semail format tocraftphishingemails. Discoveringpersonalhobbiesor interests to build rapport during pretexting.
- Identifying a
- Examples
SE Lifecycle
- Hook:
- Establishing initial contact.
- Phishing Emails
- Vishing (Voice Phishing)
- Smishing (SMS Phishing)
- Baiting
SE Lifecycle
- Hook:
- Example:
- A phishing email
disguisedas anurgentITnoticerequesting password resets. - A phone
callclaiming to be from HR asking forverificationof sensitiveinformation.
- A phishing email
- Example:
SE Lifecycle
- Play:
Extractthe desiredinformationorachievethe attack'sgoal.Executionof theattackto achieve the goal (e.g., obtaining credentials)- Credential Theft
- Privilege
Escalation - Data
Extraction - Planting
Malware
SE Lifecycle
- Play
- Example
- Convincing an employee to wire money to a fraudulent account in a Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack.
- Installing spyware via an email attachment.
- Example
SE Lifecycle
- Exit:
Avoiddetectionand either sustain access or sever the connection.- Covering Tracks:Deleting logs or hiding malware
- Sustaining Access: backdoors; long-term infiltration.
SE Lifecycle
- Exit
- Examples
- After exfiltrating sensitive data, the attacker
destroysevidenceof the intrusion. - In phishing attacks, attackers often
disablefakeloginpagesimmediatelyafter collecting credentials.
- After exfiltrating sensitive data, the attacker
- Examples
Common Social Engineering Techniques
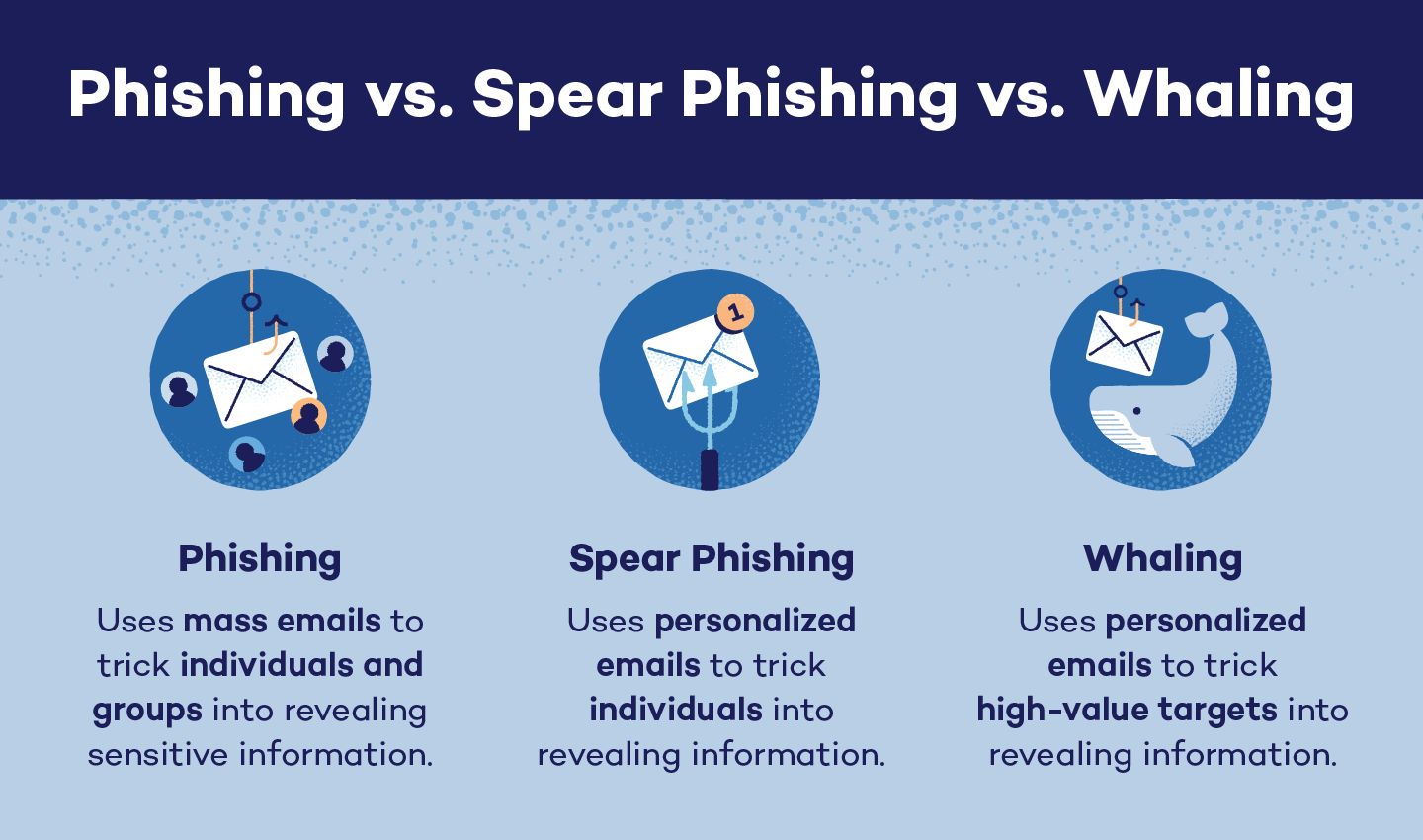
- Phishing: is one of the most
popularSocial EngineeringAttacks. The attackersendsafakeemail tostealfrom victims. PersonalData
Common Social Engineering Techniques
- Pretexting:
- Creating a
convincingidentity or scenario toextractinformation. - Creates a
fictionalbackstory

Common Social Engineering Techniques
- Baiting:
Offeringsomethingenticingtolurevictims (e.g., USB drops).- Tactic tricks the victim into:
- unintentionally
downloadingmalware into their system revealingconfidential personal organisationalinformation.
- unintentionally

Common Social Engineering Techniques
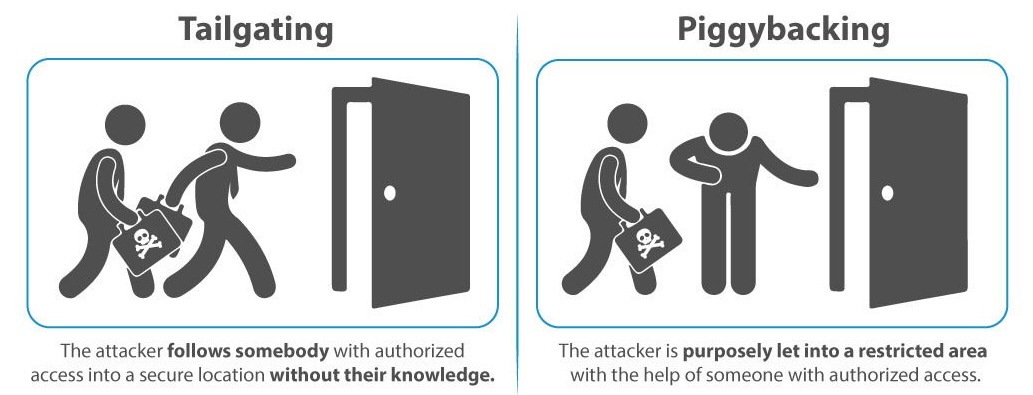
- Tailgating/Piggybacking: Gaining physical access to restricted areas by
exploitingtrust.
Common Social Engineering Techniques
- Impersonation:
Actingas atrustedindividual orauthorityfigure.Pretendingto Be TrustedExploitingAuthority andTrust- Using
FakeCredentialsand Contextual Knowledge:

Psychological Principles of Social Engineering
Psychological Principles of Social Engineering
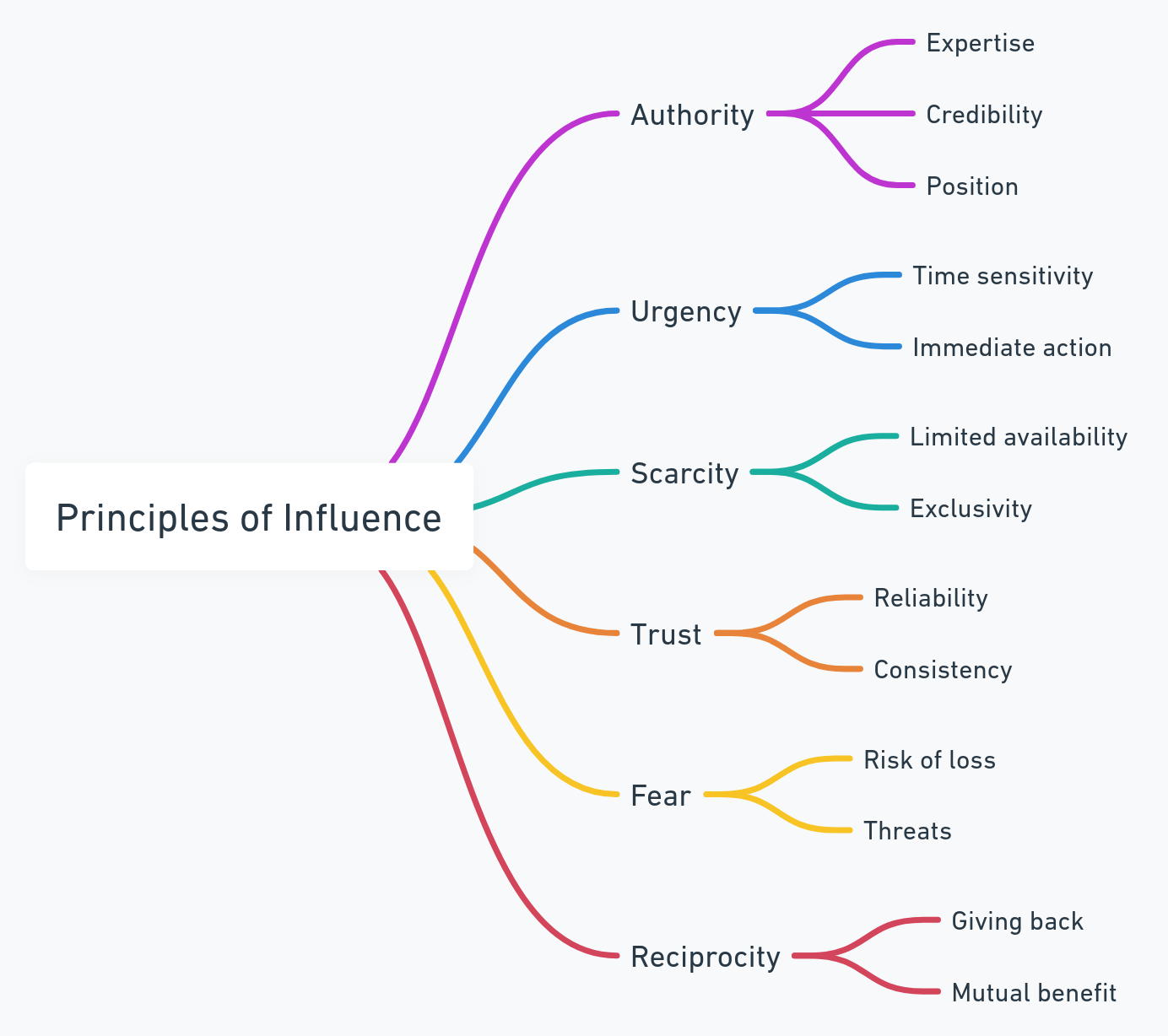
Authority
- People tend to
complywith instructions from perceivedauthorityfigures.
Example:
"I’m from IT support; I need your password to fix an issue"

Urgency
- Creating a sense of
immediateaction tobypasscriticalthin`king.
Example:
"Your account will be locked unless you reset your password now!"

Scarcity
Fearoflosingarareopportunity orresource.
Example:
-
"Limited-time offer! Click here to claim your reward."
Trust
Buildingrapportto gain confidence andcooperation.
Example:
"We’ve worked together before, right? Can you help me with this file?"
Fear and Reciprocity
Fear:
- Using
threatsor fear tocompelaction. Example: "Your data has been breached; pay to recover it."
Reciprocity:
- Exploiting the human tendency to
returnfavours. Example: "I’ve helped you before; can you send me this file?"
Real-World Applications of Social Engineering
Case Studies
- Target Data Breach (2013):
- Phishing an HVAC vendor to gain access.
- Twitter Hack (2020):
- Social engineering employees for privileged access.
- Google & Facebook (2013–2015):
- Invoice fraud through email impersonation.
- Discussion
- What enabled these attacks?
- Could they have been prevented?
How can the algorithms that personalise social media content unintentionally make users more vulnerable to social engineering attacks? Can you think of any examples where personalisation could be exploited in this way?
6. Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Technical Countermeasures
- Spam filters and email verification tools.
- Endpoint protection (e.g., USB restrictions).
Human Countermeasures
- Security awareness training.
- Regular phishing simulations.
- Policies for verifying requests (e.g., verbal confirmation).
Organisational Measures
- Clear incident response plans.
- Zero Trust approach to access control.
Checklist
Steps individuals and organisations can take to minimise risks.
Lab
- Attacks Mapping and Exploring the Social Engineering Toolkit (SET), see lab here